熟练使用 LLDB,让你调试事半功倍
发布于 2016-01-19 03:04:10 | 1277 次阅读 | 评论: 0 | 来源: 分享
LLDB C/C++调试器
LLDB 是下一代高性能的调试器,构建一组可重用的组件,覆盖很多 LLVM 项目的库,例如 Clang 表达式解析器和 LLVM 反汇编器。目前该项目还处于前期开发状态,但已经注意支持在 Mac OS X 上的 C/C++ 和 Objective-C 的开发。
LLDB是Xcode默认的调试器,它与LLVM编译器一起,带给我们更丰富的流程控制和数据检测的调试功能。平时用Xcode运行程序,实际走的都是LLDB。熟练使用LLDB,可以让你debug事半功倍。
LLDB基础知识
LLDB控制台
Xcode中内嵌了LLDB控制台,在Xcode中代码的下方,我们可以看到LLDB控制台。 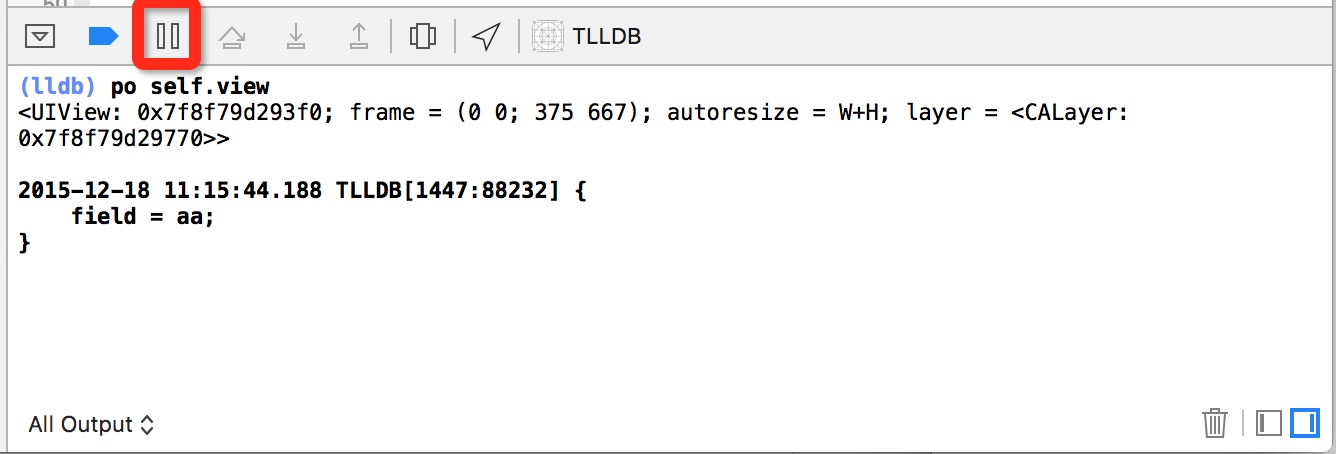 LLDB控制台平时会输出一些log信息。如果我们想输入命令调试,必须让程序进入暂停状态。让程序进入暂停状态的方式主要有2种:
LLDB控制台平时会输出一些log信息。如果我们想输入命令调试,必须让程序进入暂停状态。让程序进入暂停状态的方式主要有2种:
- 断点或者watchpoint: 在代码中设置一个断点(watchpoint),当程序运行到断点位置的时候,会进入stop状态
- 直接暂停,控制台上方有一个暂停按钮,上图红框已标出,点击即可暂停程序
LLDB语法
在使用LLDB之前,我们来先看看LLDB的语法,了解语法可以帮助我们清晰的使用LLDB:
<command> [<subcommand> [<subcommand>...]] <action> [-options [option-value]] [argument [argument...]]
一眼看上去可能比较迷茫,给大家解释一下:
<command>(命令)和<subcommand>(子命令):LLDB调试命令的名称。命令和子命令按层级结构来排列:一个命令对象为跟随其的子命令对象创建一个上下文,子命令又为其子命令创建一个上下文,依此类推。<action>:执行命令的操作<options>:命令选项<arguement>:命令的参数[]:表示命令是可选的,可以有也可以没有
举个例子,假设我们给main方法设置一个断点,我们使用下面的命令:
breakpoint set -n main
这个命令对应到上面的语法就是:
command:breakpoint表示断点命令action:set表示设置断点option:-n表示根据方法name设置断点arguement:mian表示方法名为mian
原始(raw)命令
LLDB支持不带命令选项(options)的原始(raw)命令,原始命令会将命令后面的所有东西当做参数(arguement)传递。不过很多原始命令也可以带命令选项,当你使用命令选项的时候,需要在命令选项后面加--区分命令选项和参数。
e.g: 常用的expression就是raw命令,一般情况下我们使用expression打印一个东西是这样的:
(lldb) expression count
(int) $2 = 4
当我们想打印一个对象的时候。需要使用-O命令选项,我们应该用--将命令选项和参数区分:
(lldb) expression -O -- self
<ViewController: 0x7f9000f17660>
唯一匹配原则
LLDB的命令遵循唯一匹配原则:假如根据前n个字母已经能唯一匹配到某个命令,则只写前n个字母等效于写下完整的命令。
e.g: 前面提到我设置断点的命令,我们可以使用唯一匹配原则简写,下面2条命令等效:
breakpoint set -n main
br s -n main
~/.lldbinit
LLDB有了一个启动时加载的文件~/.lldbinit,每次启动都会加载。所以一些初始化的事儿,我们可以写入~/.lldbinit中,比如给命令定义别名等。但是由于这时候程序还没有真正运行,也有部分操作无法在里面玩,比如设置断点。
LLDB命令
expression
expression命令的作用是执行一个表达式,并将表达式返回的结果输出。expression的完整语法是这样的:
expression <cmd-options> -- <expr>
<cmd-options>:命令选项,一般情况下使用默认的即可,不需要特别标明。--: 命令选项结束符,表示所有的命令选项已经设置完毕,如果没有命令选项,--可以省略<expr>: 要执行的表达式
说expression是LLDB里面最重要的命令都不为过。因为他能实现2个功能。
- 执行某个表达式。 我们在代码运行过程中,可以通过执行某个表达式来动态改变程序运行的轨迹。 假如我们在运行过程中,突然想把self.view颜色改成红色,看看效果。我们不必写下代码,重新run,只需暂停程序,用
expression改变颜色,再刷新一下界面,就能看到效果// 改变颜色 (lldb) expression -- self.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor] // 刷新界面 (lldb) expression -- (void)[CATransaction flush] - 将返回值输出。 也就是说我们可以通过
expression来打印东西。 假如我们想打印self.view:
(lldb) expression -- self.view
(UIView *) $1 = 0x00007fe322c18a10
p & print & call
一般情况下,我们直接用expression还是用得比较少的,更多时候我们用的是p、print、call。这三个命令其实都是expression --的别名(--表示不再接受命令选项,详情见前面原始(raw)命令这一节)
print: 打印某个东西,可以是变量和表达式p: 可以看做是print的简写call: 调用某个方法。
表面上看起来他们可能有不一样的地方,实际都是执行某个表达式(变量也当做表达式),将执行的结果输出到控制台上。所以你可以用p调用某个方法,也可以用call打印东西 e.g: 下面代码效果相同:
(lldb) expression -- self.view
(UIView *) $5 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
(lldb) p self.view
(UIView *) $6 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
(lldb) print self.view
(UIView *) $7 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
(lldb) call self.view
(UIView *) $8 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
(lldb) e self.view
(UIView *) $9 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
根据唯一匹配原则,如果你没有自己添加特殊的命令别名。
e也可以表示expression的意思。原始命令默认没有命令选项,所以e也能带给你同样的效果
po
我们知道,OC里所有的对象都是用指针表示的,所以一般打印的时候,打印出来的是对象的指针,而不是对象本身。如果我们想打印对象。我们需要使用命令选项:-O。为了更方便的使用,LLDB为expression -O --定义了一个别名:po
(lldb) expression -- self.view
(UIView *) $13 = 0x00007fb2a40344a0
(lldb) expression -O -- self.view
<UIView: 0x7fb2a40344a0; frame = (0 0; 375 667); autoresize = W+H; layer = <CALayer: 0x7fb2a4018c80>>
(lldb) po self.view
<UIView: 0x7fb2a40344a0; frame = (0 0; 375 667); autoresize = W+H; layer = <CALayer: 0x7fb2a4018c80>>
还有其他很多命令选项,不过我们一般用得比较少,所以我就不具体的一一介绍了,如果想了解,在LLDB控制台上输入:
help expression即可查到expression所有的信息
thread
thread backtrace & bt
有时候我们想要了解线程堆栈信息,可以使用thread backtrace thread backtrace作用是将线程的堆栈打印出来。我们来看看他的语法
thread backtrace [-c <count>] [-s <frame-index>] [-e <boolean>]
thread backtrace后面跟的都是命令选项:
-c:设置打印堆栈的帧数(frame)-s:设置从哪个帧(frame)开始打印-e:是否显示额外的回溯
实际上这些命令选项我们一般不需要使用。
e.g: 当发生crash的时候,我们可以使用thread backtrace查看堆栈调用
(lldb) thread backtrace
* thread #1: tid = 0xdd42, 0x000000010afb380b libobjc.A.dylib`objc_msgSend + 11, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=EXC_I386_GPFLT)
frame #0: 0x000000010afb380b libobjc.A.dylib`objc_msgSend + 11
* frame #1: 0x000000010aa9f75e TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad](self=0x00007fa270e1f440, _cmd="viewDidLoad") + 174 at ViewController.m:23
frame #2: 0x000000010ba67f98 UIKit`-[UIViewController loadViewIfRequired] + 1198
frame #3: 0x000000010ba682e7 UIKit`-[UIViewController view] + 27
frame #4: 0x000000010b93eab0 UIKit`-[UIWindow addRootViewControllerViewIfPossible] + 61
frame #5: 0x000000010b93f199 UIKit`-[UIWindow _setHidden:forced:] + 282
frame #6: 0x000000010b950c2e UIKit`-[UIWindow makeKeyAndVisible] + 42
我们可以看到crash发生在-[ViewController viewDidLoad]中的第23行,只需检查这行代码是不是干了什么非法的事儿就可以了。
LLDB还为backtrace专门定义了一个别名:bt,他的效果与thread backtrace相同,如果你不想写那么长一串字母,直接写下bt即可:
(lldb) bt
thread return
Debug的时候,也许会因为各种原因,我们不想让代码执行某个方法,或者要直接返回一个想要的值。这时候就该thread return上场了。
thread return [<expr>]
thread return可以接受一个表达式,调用命令之后直接从当前的frame返回表达式的值。
e.g: 我们有一个someMethod方法,默认情况下是返回YES。我们想要让他返回NO
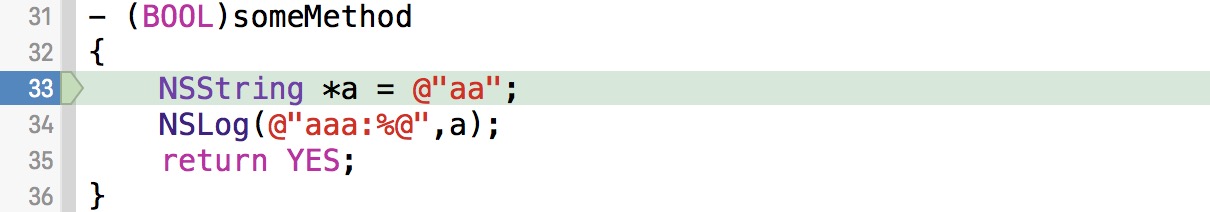
我们只需在方法的开始位置加一个断点,当程序中断的时候,输入命令即可:
(lldb) thread return NO
效果相当于在断点位置直接调用return NO;,不会执行断点后面的代码
c & n & s & finish
一般在调试程序的时候,我们经常用到下面这4个按钮:
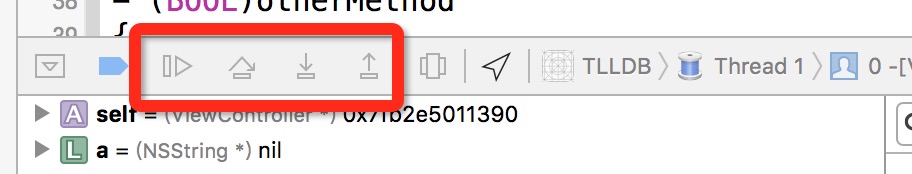
用触摸板的孩子们可能会觉得点击这4个按钮比较费劲。其实LLDB命令也可以完成上面的操作,而且如果不输入命令,直接按Enter键,LLDB会自动执行上次的命令。按一下Enter就能达到我们想要的效果,有木有顿时感觉逼格满满的!!! 我们来看看对应这4个按钮的LLDB命令:
c/continue/thread continue: 这三个命令效果都等同于上图中第一个按钮的。表示程序继续运行n/next/thread step-over: 这三个命令效果等同于上图第二个按钮。表示单步运行s/step/thread step-in: 这三个命令效果等同于上图第三个按钮。表示进入某个方法finish/step-out: 这两个命令效果等同于第四个按钮。表示直接走完当前方法,返回到上层frame
thread其他不常用的命令
thread 相关的还有其他一些不常用的命令,这里就简单介绍一下即可,如果需要了解更多,可以使用命令help thread查阅
thread jump: 直接让程序跳到某一行。由于ARC下编译器实际插入了不少retain,release命令。跳过一些代码不执行很可能会造成对象内存混乱发生crash。thread list: 列出所有的线程thread select: 选择某个线程thread until: 传入一个line的参数,让程序执行到这行的时候暂停thread info: 输出当前线程的信息
frame
前面我们提到过很多次frame(帧)。可能有的朋友对frame这个概念还不太了解。随便打个断点
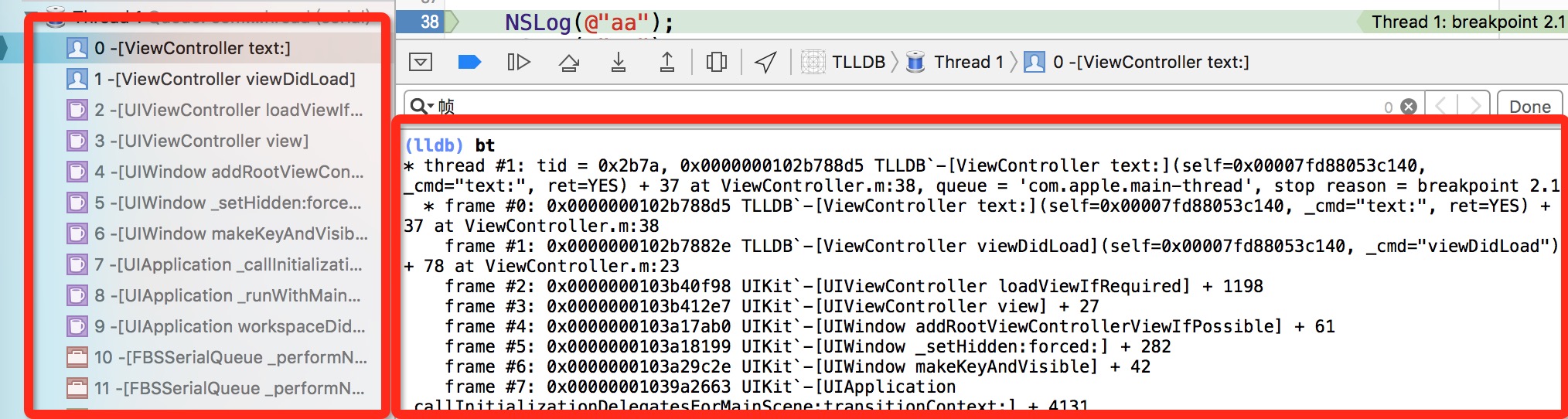
我们在控制台上输入命令bt,可以打印出来所有的frame。如果仔细观察,这些frame和左边红框里的堆栈是一致的。平时我们看到的左边的堆栈就是frame。
frame variable
平时Debug的时候我们经常做的事就是查看变量的值,通过frame variable命令,可以打印出当前frame的所有变量
(lldb) frame variable
(ViewController *) self = 0x00007fa158526e60
(SEL) _cmd = "text:"
(BOOL) ret = YES
(int) a = 3
可以看到,他将self,_cmd,ret,a等本地变量都打印了出来
如果我们要需要打印指定变量,也可以给frame variable传入参数:
(lldb) frame variable self->_string
(NSString *) self->_string = nil
不过frame variable只接受变量作为参数,不接受表达式,也就是说我们无法使用frame variable self.string,因为self.string是调用string的getter方法。所以一般打印指定变量,我更喜欢用p或者po。
其他不常用命令
一般frame variable打印所有变量用得比较多,frame还有2个不怎么常用的命令:
frame info: 查看当前frame的信息
(lldb) frame info
frame #0: 0x0000000101bf87d5 TLLDB`-[ViewController text:](self=0x00007fa158526e60, _cmd="text:", ret=YES) + 37 at ViewController.m:38
frame select: 选择某个frame
(lldb) frame select 1
frame #1: 0x0000000101bf872e TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad](self=0x00007fa158526e60, _cmd="viewDidLoad") + 78 at ViewController.m:23
20
21 - (void)viewDidLoad {
22 [super viewDidLoad];
-> 23 [self text:YES];
24 NSLog(@"1");
25 NSLog(@"2");
26 NSLog(@"3");
当我们选择frame 1的时候,他会把frame1的信息和代码打印出来。不过一般我都是直接在Xcode左边点击某个frame,这样更方便
breakpoint
调试过程中,我们用得最多的可能就是断点了。LLDB中的断点命令也非常强大
breakpoint set
breakpoint set命令用于设置断点,LLDB提供了很多种设置断点的方式:
使用-n根据方法名设置断点:
e.g: 我们想给所有类中的viewWillAppear:设置一个断点:
(lldb) breakpoint set -n viewWillAppear:
Breakpoint 13: 33 locations.
使用-f指定文件
e.g: 我们只需要给ViewController.m文件中的viewDidLoad设置断点:
(lldb) breakpoint set -f ViewController.m -n viewDidLoad
Breakpoint 22: where = TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad] + 20 at ViewController.m:22, address = 0x000000010272a6f4
这里需要注意,如果方法未写在文件中(比如写在category文件中,或者父类文件中),指定文件之后,将无法给这个方法设置断点。
使用-l指定文件某一行设置断点
e.g: 我们想给ViewController.m第38行设置断点
(lldb) breakpoint set -f ViewController.m -l 38
Breakpoint 23: where = TLLDB`-[ViewController text:] + 37 at ViewController.m:38, address = 0x000000010272a7d5
使用-c设置条件断点
e.g: text:方法接受一个ret的参数,我们想让ret == YES的时候程序中断:
(lldb) breakpoint set -n text: -c ret == YES
Breakpoint 7: where = TLLDB`-[ViewController text:] + 30 at ViewController.m:37, address = 0x0000000105ef37ce
使用-o设置单次断点
e.g: 如果刚刚那个断点我们只想让他中断一次:
(lldb) breakpoint set -n text: -o
'breakpoint 3': where = TLLDB`-[ViewController text:] + 30 at ViewController.m:37, address = 0x000000010b6f97ce
breakpoint command
有的时候我们可能需要给断点添加一些命令,比如每次走到这个断点的时候,我们都需要打印self对象。我们只需要给断点添加一个po self命令,就不用每次执行断点再自己输入po self了
breakpoint command add
breakpoint command add命令就是给断点添加命令的命令。
e.g: 假设我们需要在ViewController的viewDidLoad中查看self.view的值 我们首先给-[ViewController viewDidLoad]添加一个断点
(lldb) breakpoint set -n "-[ViewController viewDidLoad]"
'breakpoint 3': where = TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad] + 20 at ViewController.m:23, address = 0x00000001055e6004
可以看到添加成功之后,这个breakpoint的id为3,然后我们给他增加一个命令:po self.view
(lldb) breakpoint command add -o "po self.view" 3
-o完整写法是--one-liner,表示增加一条命令。3表示对id为3的breakpoint增加命令。 添加完命令之后,每次程序执行到这个断点就可以自动打印出self.view的值了
如果我们一下子想增加多条命令,比如我想在viewDidLoad中打印当前frame的所有变量,但是我们不想让他中断,也就是在打印完成之后,需要继续执行。我们可以这样玩:
(lldb) breakpoint command add 3
Enter your debugger command(s). Type 'DONE' to end.
> frame variable
> continue
> DONE
输入breakpoint command add 3对断点3增加命令。他会让你输入增加哪些命令,输入’DONE’表示结束。这时候你就可以输入多条命令了
多次对同一个断点添加命令,后面命令会将前面命令覆盖
breakpoint command list
如果想查看某个断点已有的命令,可以使用breakpoint command list。 e.g: 我们查看一下刚刚的断点3已有的命令
(lldb) breakpoint command list 3
'breakpoint 3':
Breakpoint commands:
frame variable
continue
可以看到一共有2条命令,分别为frame variable和continue
breakpoint command delete
有增加就有删除,breakpoint command delete可以让我们删除某个断点的命令 e.g: 我们将断点3中的命令删除:
(lldb) breakpoint command delete 3
(lldb) breakpoint command list 3
Breakpoint 3 does not have an associated command.
可以看到删除之后,断点3就没有命令了
breakpoint list
如果我们想查看已经设置了哪些断点,可以使用breakpoint list e.g:
(lldb) breakpoint list
Current breakpoints:
4: name = '-[ViewController viewDidLoad]', locations = 1, resolved = 1, hit count = 0
4.1: where = TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad] + 20 at ViewController.m:23, address = 0x00000001055e6004, resolved, hit count = 0
我们可以看到当前只有一个断点,打在-[ViewController viewDidLoad]上,id是4
breakpoint disable/enable
有的时候我们可能暂时不想要某个断点,可以使用breakpoint disable让某个断点暂时失效 e.g: 我们来让刚刚的断点4失效
(lldb) breakpoint disable 4
1 breakpoints disabled.
输入完命令之后,显示断点已经失效
当我们又需要这个断点的时候,可以使用breakpoint enable再次让他生效 e.g: 重新启用断点4
(lldb) breakpoint enable 4
1 breakpoints enabled.
breakpoint delete
如果我们觉得这个断点以后再也用不上了,可以用breakpoint delete直接删除断点. e.g: 删除断点4
(lldb) breakpoint delete 4
1 breakpoints deleted; 0 breakpoint locations disabled.
如果我们想删除所有断点,只需要不指定breakpoint delete参数即可
(lldb) breakpoint delete
About to delete all breakpoints, do you want to do that?: [Y/n] y
All breakpoints removed. (1 breakpoint)
删除的时候他会提示你,是不是真的想删除所有断点,需要你再次输入Y确认。如果想直接删除,不需要他的提示,使用-f命令选项即可
(lldb) breakpoint delete -f
All breakpoints removed. (1 breakpoint)
实际平时我们真正使用
breakpoint命令反而比较少,因为Xcode已经内置了断点工具。我们可以直接在代码上打断点,可以在断点工具栏里面查看编辑断点,这比使用LLDB命令方便很多。不过了解LLDB相关命令可以让我们对断点理解更深刻。 如果你想了解怎么使用Xcode设置断点,可以阅读这篇文章《Xcode中断点的威力》
watchpoint
breakpoint有一个孪生兄弟watchpoint。如果说breakpoint是对方法生效的断点,watchpoint就是对地址生效的断点
如果我们想要知道某个属性什么时候被篡改了,我们该怎么办呢?有人可能会说对setter方法打个断点不就行了么?但是如果更改的时候没调用setter方法呢? 这时候最好的办法就是用watchpoint。我们可以用他观察这个属性的地址。如果地址里面的东西改变了,就让程序中断
watchpoint set
watchpoint set命令用于添加一个watchpoint。只要这个地址中的内容变化了,程序就会中断。
watchpoint set variable
一般情况下,要观察变量或者属性,使用watchpoint set variable命令即可 e.g: 观察self->_string
(lldb) watchpoint set variable self->_string
Watchpoint created: Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x7fcf3959c418 size = 8 state = enabled type = w
watchpoint spec = 'self->_string'
new value: 0x0000000000000000
watchpoint set variable传入的是变量名。需要注意的是,这里不接受方法,所以不能使用watchpoint set variable self.string,因为self.string调用的是string的getter方法
watchpoint set expression
如果我们想直接观察某个地址,可以使用watchpoint set expression e.g: 我们先拿到_model的地址,然后对地址设置一个watchpoint
(lldb) p &_model
(Modek **) $3 = 0x00007fe0dbf23280
(lldb) watchpoint set expression 0x00007fe0dbf23280
Watchpoint created: Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x7fe0dbf23280 size = 8 state = enabled type = w
new value: 0
watchpoint command
跟breakpoint类似,在watchpoint中也可以添加命令
watchpoint command add
我们来看看怎么给watchpoint添加命令:
首先,我们设置一个watchpoint:
(lldb) watchpoint set variable _string
Watchpoint created: Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x7fe4e1444760 size = 8 state = enabled type = w
watchpoint spec = '_string'
new value: 0x0000000000000000
可以看到这个watchpoint的id是1。我们可以用watchpoint command add -o添加单条命令
watchpoint command add -o 'bt' 1
我们在watchpoint停下来的时候,打印了他的线程信息。
我们也可以一次添加多条命令:
(lldb) watchpoint command add 1
Enter your debugger command(s). Type 'DONE' to end.
> bt
> continue
> DONE
可以看到watchpoint的使用方法跟breakpoint几乎一模一样。
watchpoint command list
我们可以用watchpoint command list列出某个watchpoint所有的command
(lldb) watchpoint command list 1
Watchpoint 1:
watchpoint commands:
bt
continue
watchpoint command delete
我们也可以用watchpoint command delete删除某个watchpoint所有的command
(lldb) watchpoint command delete 1
(lldb) watchpoint command list 1
Watchpoint 1 does not have an associated command.
watchpoint list
如果我们想看当前所有watchpoint,可以使用watchpoint list:
(lldb) watchpoint list
Number of supported hardware watchpoints: 4
Current watchpoints:
Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x7fe9f9f28e30 size = 8 state = enabled type = w
watchpoint spec = '_string'
old value: 0x0000000000000000
new value: 0x000000010128e0d0
可以看到,只有一个watchpoint。
watchpoint disable
当我们不想让某个watchpoint生效的时候,可以用watchpoint disable:
(lldb) watchpoint disable 1
1 watchpoints disabled.
再次查看这个watchpoint,可以看到他的state已经变为了disabled
(lldb) watchpoint list
Number of supported hardware watchpoints: 4
Current watchpoints:
Watchpoint 1: addr = 0x7fe9f9f28e30 size = 8 state = disabled type = w
watchpoint spec = '_string'
old value: 0x0000000000000000
new value: 0x000000010128e0d0
watchpoint enable
过了一会,我们又要用这个watchpoint了,这时候可以使用watchpoint enable:
(lldb) watchpoint enable 1
1 watchpoints enabled.
watchpoint delete
如果我们觉得再也用不着这个watchpoint了,可以用watchpoint delete将他删除:
(lldb) watchpoint delete 1
1 watchpoints deleted.
(lldb) watchpoint list
Number of supported hardware watchpoints: 4
No watchpoints currently set.
删除之后,我们可以看到watchpoint list里面已经没有watchpoint1了
如果有很多个watchpoint,我们想全都干掉,只需要不指定具体哪个watchpoint即可:
(lldb) watchpoint delete
About to delete all watchpoints, do you want to do that?: [Y/n] y
All watchpoints removed. (2 watchpoints)
target
target modules lookup(image lookup)
对于target这个命令,我们用得最多的可能就是target modules lookup。由于LLDB给target modules取了个别名image,所以这个命令我们又可以写成image lookup。
image lookup –address
当我们有一个地址,想查找这个地址具体对应的文件位置,可以使用image lookup --address,简写为image lookup -a e.g: 当我们发生一个crash
2015-12-17 14:51:06.301 TLLDB[25086:246169] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSRangeException', reason: '*** -[__NSArray0 objectAtIndex:]: index 1 beyond bounds for empty NSArray'
*** First throw call stack:
(
0 CoreFoundation 0x000000010accde65 __exceptionPreprocess + 165
1 libobjc.A.dylib 0x000000010a746deb objc_exception_throw + 48
2 CoreFoundation 0x000000010ac7c395 -[__NSArray0 objectAtIndex:] + 101
3 TLLDB 0x000000010a1c3e36 -[ViewController viewDidLoad] + 86
4 UIKit 0x000000010b210f98 -[UIViewController loadViewIfRequired] + 1198
5 UIKit 0x000000010b2112e7 -[UIViewController view] + 27
我们可以看到是由于-[__NSArray0 objectAtIndex:]:超出边界而导致的crash,但是objectAtIndex:的代码到底在哪儿呢?
(lldb) image lookup -a 0x000000010a1c3e36
Address: TLLDB[0x0000000100000e36] (TLLDB.__TEXT.__text + 246)
Summary: TLLDB`-[ViewController viewDidLoad] + 86 at ViewController.m:32
根据0x000000010a1c3e36 -[ViewController viewDidLoad]里面的地址,使用image lookup --address查找,我们可以看到代码位置在ViewController.m里面的32行
image lookup –name
当我们想查找一个方法或者符号的信息,比如所在文件位置等。我们可以使用image lookup --name,简写为image lookup -n。
e.g: 刚刚遇到的真问题,某个第三方SDK用了一个我们项目里原有的第三方库,库里面对NSDictionary添加了category。也就是有2个class对NSDictionary添加了名字相同的category,项目中调用自己的category的地方实际走到了第三方SDK里面去了。最大的问题是,这2个同名category方法行为并不一致,导致出现bug
现在问题来了,怎么寻找到底是哪个第三方SDK?方法完全包在.a里面。
其实只需使用image lookup -n即可:
(lldb) image lookup -n dictionaryWithXMLString:
2 matches found in /Users/jiangliancheng/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/VideoIphone-aivsnqmlwjhxapdlvmdmrubbdxpq/Build/Products/Debug-iphoneos/BaiduIphoneVideo.app/BaiduIphoneVideo:
Address: BaiduIphoneVideo[0x00533a7c] (BaiduIphoneVideo.__TEXT.__text + 5414908)
Summary: BaiduIphoneVideo`+[NSDictionary(SAPIXmlDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:] at XmlDictionary.m
Module: file = "/Users/jiangliancheng/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/VideoIphone-aivsnqmlwjhxapdlvmdmrubbdxpq/Build/Products/Debug-iphoneos/BaiduIphoneVideo.app/BaiduIphoneVideo", arch = "armv7"
CompileUnit: id = {0x00000000}, file = "/Users/jiangliancheng/Development/Work/iOS_ShareLib/SharedLib/Srvcs/BDPassport4iOS/BDPassport4iOS/SAPI/Extensive/ThirdParty/XMLDictionary/XmlDictionary.m", language = "Objective-C"
Function: id = {0x23500000756}, name = "+[NSDictionary(SAPIXmlDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:]", range = [0x005a6a7c-0x005a6b02)
FuncType: id = {0x23500000756}, decl = XmlDictionary.m:189, clang_type = "NSDictionary *(NSString *)"
Blocks: id = {0x23500000756}, range = [0x005a6a7c-0x005a6b02)
LineEntry: [0x005a6a7c-0x005a6a98): /Users/jiangliancheng/Development/Work/iOS_ShareLib/SharedLib/Srvcs/BDPassport4iOS/BDPassport4iOS/SAPI/Extensive/ThirdParty/XMLDictionary/XmlDictionary.m
Symbol: id = {0x0000f2d5}, range = [0x005a6a7c-0x005a6b04), name="+[NSDictionary(SAPIXmlDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:]"
Variable: id = {0x23500000771}, name = "self", type = "Class", location = [sp+32], decl =
Variable: id = {0x2350000077e}, name = "_cmd", type = "SEL", location = [sp+28], decl =
Variable: id = {0x2350000078b}, name = "string", type = "NSString *", location = [sp+24], decl = XmlDictionary.m:189
Variable: id = {0x23500000799}, name = "data", type = "NSData *", location = [sp+20], decl = XmlDictionary.m:192
Address: BaiduIphoneVideo[0x012ee160] (BaiduIphoneVideo.__TEXT.__text + 19810016)
Summary: BaiduIphoneVideo`+[NSDictionary(XMLDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:] at XMLDictionary.m
Module: file = "/Users/jiangliancheng/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/VideoIphone-aivsnqmlwjhxapdlvmdmrubbdxpq/Build/Products/Debug-iphoneos/BaiduIphoneVideo.app/BaiduIphoneVideo", arch = "armv7"
CompileUnit: id = {0x00000000}, file = "/Users/wingle/Workspace/qqlive4iphone/iphone_4.0_fabu_20150601/Common_Proj/mobileTAD/VIDEO/Library/Third Party/XMLDictionary/XMLDictionary.m", language = "Objective-C"
Function: id = {0x79900000b02}, name = "+[NSDictionary(XMLDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:]", range = [0x01361160-0x0136119a)
FuncType: id = {0x79900000b02}, decl = XMLDictionary.m:325, clang_type = "NSDictionary *(NSString *)"
Blocks: id = {0x79900000b02}, range = [0x01361160-0x0136119a)
LineEntry: [0x01361160-0x01361164): /Users/wingle/Workspace/qqlive4iphone/iphone_4.0_fabu_20150601/Common_Proj/mobileTAD/VIDEO/Library/Third Party/XMLDictionary/XMLDictionary.m
Symbol: id = {0x0003a1e9}, range = [0x01361160-0x0136119c), name="+[NSDictionary(XMLDictionary) dictionaryWithXMLString:]"
Variable: id = {0x79900000b1e}, name = "self", type = "Class", location = r0, decl =
Variable: id = {0x79900000b2c}, name = "_cmd", type = "SEL", location = r1, decl =
Variable: id = {0x79900000b3a}, name = "string", type = "NSString *", location = r2, decl = XMLDictionary.m:325
Variable: id = {0x79900000b4a}, name = "data", type = "NSData *", location = r2, decl = XMLDictionary.m:327
东西有点多,我们只需关注里面的file这一行:
CompileUnit: id = {0x00000000}, file = "/Users/jiangliancheng/Development/Work/iOS_ShareLib/SharedLib/Srvcs/BDPassport4iOS/BDPassport4iOS/SAPI/Extensive/ThirdParty/XMLDictionary/XmlDictionary.m", language = "Objective-C"
CompileUnit: id = {0x00000000}, file = "/Users/wingle/Workspace/qqlive4iphone/iphone_4.0_fabu_20150601/Common_Proj/mobileTAD/VIDEO/Library/Third Party/XMLDictionary/XMLDictionary.m", language = "Objective-C"
可以清晰的看到,LLDB给我们找出来了这个方法的位置。 当然这个命令也可以找到方法的其他相关信息,比如参数等.
image lookup –type
当我们想查看一个类型的时候,可以使用image lookup --type,简写为image lookup -t:
e.g: 我们来看看Model的类型:
(lldb) image lookup -t Model
Best match found in /Users/jiangliancheng/Library/Developer/Xcode/DerivedData/TLLDB-beqoowskwzbttrejseahdoaivpgq/Build/Products/Debug-iphonesimulator/TLLDB.app/TLLDB:
id = {0x30000002f}, name = "Model", byte-size = 32, decl = Modek.h:11, clang_type = "@interface Model : NSObject{
NSString * _bb;
NSString * _cc;
NSString * _name;
}
@property ( getter = name,setter = setName:,readwrite,nonatomic ) NSString * name;
@end
"
可以看到,LLDB把Model这个class的所有属性和成员变量都打印了出来,当我们想了解某个类的时候,直接使用image lookup -t即可
target stop-hook
我们知道,用LLDB debug,大多数时候需要让程序stop,不管用breakpoint还是用watchpoint。
target stop-hook命令就是让你可以在每次stop的时候去执行一些命令
target stop-hook只对breakpoint和watchpoint的程序stop生效,直接点击Xcode上的pause或者debug view hierarchy不会生效
target stop-hook add & display
假如我们想在每次程序stop的时候,都用命令打印当前frame的所有变量。我们可以添加一个stop-hook:
(lldb) target stop-hook add -o "frame variable"
Stop hook #4 added.
target stop-hook add表示添加stop-hook,-o的全称是--one-liner,表示添加一条命令。
我们看一下,当执行到一个断点的时候会发生什么?
- Hook 1 (frame variable)
(ViewController *) self = 0x00007fd55b12e380
(SEL) _cmd = "viewDidLoad"
(NSMutableURLRequest *) request = 0x00007fd55b1010c0
在程序stop的时候,他会自动执行frame variable,打印出了所有的变量。
大多情况下,我们在stop的时候可能想要做的是打印一个东西。正常情况我们需要用target stop-hook add -o "p xxx",LLDB提供了一个更简便的命令display。
e.g: 下面2行代码效果相同
(lldb) target stop-hook add -o "p self.view"
(lldb) display self.view
也可以用
display来执行某一个命令。p,e,expression是等效的。
target stop-hook list
当添加完stop-hook之后,我们想看当前所有的stop-hook怎么办呢?使用stop-hook list
(lldb) target stop-hook list
Hook: 4
State: enabled
Commands:
frame variable
Hook: 5
State: enabled
Commands:
expression self.view
Hook: 6
State: enabled
Commands:
expr -- self.view
我们可以看到,我们添加了4个stop-hook,每个stop-hook都有一个id,他们分别是4,5,6
target stop-hook delete & undisplay
有添加的命令,当然也就有删除的命令。使用target stop-hook delete可以删除stop-hook,如果你觉得这个命令有点长,懒得敲。你也可以用undisplay
(lldb) target stop-hook delete 4
(lldb) undisplay 5
我们用target stop-hook delete和undisplay分别删除了id为4和5的stop-hook
target stop-hook disable/enable
当我们暂时想让某个stop-hook失效的时候,可以使用target stop-hook disable
(lldb) target stop-hook disable 8
如果我们想让所有的stop-hook失效,只需不传入stop-hookid即可:
(lldb) target stop-hook disable
有disable就有enable,我们又想让stop-hook生效了。可以使用target stop-hook enable
(lldb) target stop-hook enable 8
同理,不传入参数表示让所有stop-hook生效
(lldb) target stop-hook enable
Extension
前几天@兔be南玻1在微博上给出一个小技巧。LLDB中@import UIKit即可打印frame等变量(默认情况下打不出来)微博链接。
(lldb) p self.view.frame
error: property 'frame' not found on object of type 'UIView *'
error: 1 errors parsing expression
(lldb) e @import UIKit
(lldb) p self.view.frame
(CGRect) $0 = (origin = (x = 0, y = 0), size = (width = 375, height = 667))
由于每次run Xcode,LLDB的东西都会被清空。所以每次run你都需要在LLDB中输入e @import UIKit才能使用这个方便的功能,有点麻烦呀!
之后有人提出了比较方便的一个办法。给UIApplicationMain设置一个断点,在断点中添加执行e @import UIKit。 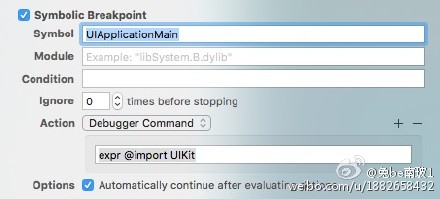 这种方法非常方便,不用自己输入了,但是断点我们可能会误删,而且断点是对应工程的。换一个工程又得重新打一个这样的断点。还是有点麻烦。有没有更简便的方法呢?
这种方法非常方便,不用自己输入了,但是断点我们可能会误删,而且断点是对应工程的。换一个工程又得重新打一个这样的断点。还是有点麻烦。有没有更简便的方法呢?
我们首先想到的是LLDB在每次启动的时候都会load ‘~/.lldbinit’文件。在这里面执行e @import UIKit不就行了么?不会被误删,对每个工程都有效!
然而想法是美好的,现实却是残酷的!因为UIKit这个库是在target中。而load ‘~/.lldbinit’的时候target还没创建。所以无法import UIKit。stackoverflow详细解释
这时候我们又想到,可不可以在’~/.lldbinit’中给UIApplicationMain设置一个断点,在断点中添加执行e @import UIKit呢?
答案是不行。原因跟前面一样,load ‘~/.lldbinit’执行时间太早。断点是依赖target的,target还未创建,断点加不上去。好事多磨,道路坎坷呀~~~
后来我们又想到用stop-hook行不行呢?stop-hook不依赖target。一般我们p frame的时候,都需要先stop,理论上是可行的
事实证明stop-hook的方法完全ok。只需要在’~/.lldbinit’中添加这2条命令即可:
display @import UIKit
target stop-hook add -o "target stop-hook disable"
- 命令1:使用
display表示在stop的时候执行@import UIKit - 命令2:由于我们只需要执行一次
@import UIKit,所以执行完成之后,执行target stop-hook disable,使原有的所有stop-hook失效
这个命令有个缺陷,直接点击Xcode上的
pause和debug view hierarchy,stop-hook不会生效。正在探索有没有更好的办法完成@import UIKit,如果你想到了,可以联系我~
target symbols add(add-dsym)
说这个命令之前,先简单解释一下dSYM文件。程序运行的时候,都会编译成二进制文件。因为计算机只识别二进制文件,那为什么我们还能在代码上打断点?
这主要是因为在编译的时候Xcode会生成dSYM文件,dSYM文件记录了哪行代码对应着哪些二进制,这样我们对代码打断点就会对应到二进制上。dSYM详细资料
当Xcode找不着dSYM文件的时候,我们就无法对代码打断点,进行调试。target symbols add命令的作用就是让我们可以手动的将dSYM文件添加上去。LLBD对这个命令起了一个别名: add-dsym
e.g: 当我们对接framework的时候,如果只有framework代码,没有工程代码,能不能debug呢?其实我们只需要拿到工程的ipa和dSYM文件,就可以debug了,通过Attach to Process,使用命令add-dsym将dSYM文件加入target,即可只debug framework,不需要工程的代码
add-dsym ~/.../XXX.dSYM
详细细节可以查看iOS中framework的联调
help & apropos
LLDB的命令其实还有很多,很多命令我也没玩过。就算玩过的命令,我们也非常容易忘记,下次可能就不记得是怎么用的了。还好LLDB给我们提供了2个查找命令的命令:help & apropos
help
直接在LLDB中输入help。可以查看所有的LLDB命令
(lldb) help
Debugger commands:
apropos -- Find a list of debugger commands related to a particular
word/subject.
breakpoint -- A set of commands for operating on breakpoints. Also see
_regexp-break.
help -- Show a list of all debugger commands, or give details
about specific commands.
script -- Pass an expression to the script interpreter for
evaluation and return the results. Drop into the
interactive interpreter if no expression is given.
settings -- A set of commands for manipulating internal settable
debugger variables.
source -- A set of commands for accessing source file information
target -- A set of commands for operating on debugger targets.
thread -- A set of commands for operating on one or more threads
within a running process.
type -- A set of commands for operating on the type system
version -- Show version of LLDB debugger.
watchpoint -- A set of commands for operating on watchpoints.
....(东西太多,只截取了一部分)
如果我们想看具体某一个命令的详细用法,可以使用help <command-name> e.g: 我们查看watchpoint命令
(lldb) help watchpoint
The following subcommands are supported:
command -- A set of commands for adding, removing and examining bits of
code to be executed when the watchpoint is hit (watchpoint
'commmands').
delete -- Delete the specified watchpoint(s). If no watchpoints are
specified, delete them all.
disable -- Disable the specified watchpoint(s) without removing it/them.
If no watchpoints are specified, disable them all.
enable -- Enable the specified disabled watchpoint(s). If no watchpoints
are specified, enable all of them.
ignore -- Set ignore count on the specified watchpoint(s). If no
watchpoints are specified, set them all.
list -- List all watchpoints at configurable levels of detail.
modify -- Modify the options on a watchpoint or set of watchpoints in
the executable. If no watchpoint is specified, act on the
last created watchpoint. Passing an empty argument clears the
modification.
set -- A set of commands for setting a watchpoint.
apropos
有的时候,我们可能并不能完全记得某个命令,如果只记得命令中的某个关键字。这时候我们可以使用apropos搜索相关命令信息。
e.g: 我们想使用stop-hook的命令,但是已经不记得stop-hook命令是啥样了
(lldb) apropos stop-hook
The following built-in commands may relate to 'stop-hook':
_regexp-display -- Add an expression evaluation stop-hook.
_regexp-undisplay -- Remove an expression evaluation stop-hook.
target stop-hook -- A set of commands for operating on debugger
target stop-hooks.
target stop-hook add -- Add a hook to be executed when the target stops.
target stop-hook delete -- Delete a stop-hook.
target stop-hook disable -- Disable a stop-hook.
target stop-hook enable -- Enable a stop-hook.
target stop-hook list -- List all stop-hooks.
可以看到使用apropos stop-hook搜索一下,即可将所有stop-hook相关命令搜索出来
常用的Debug快捷键
debug的时候,使用快捷键是一个很好的习惯,我简单列举了几个debug的快捷键
| 功能 | 命令 |
|---|---|
| 暂停/继续 | cmd + ctrl + Y |
| 断点失效/生效 | cmd + Y |
| 控制台显示/隐藏 | cmd + shift + Y |
| 光标切换到控制台 | cmd + shift + C |
| 清空控制台 | cmd + K |
| step over | F6 |
| step into | F7 |
| step out | F8 |
End
东西有点多,感谢大家耐心看完这篇文章。LLDB命令非常多,有很多LLDB命令我也没玩过。这些命令我们不一定要完全记住,只要有个印象LLDB可以实现哪些功能就可以了。具体用的时候再用help或者apropos查找。